Language Matters: A Recovery Scientist Explains the Impact of Our Words from The Fix
By Olivia Pennelle
If a person has internalized the negative stereotypes associated with being “an addict,” are they more likely to have a fixed mindset and believe they cannot improve or change?
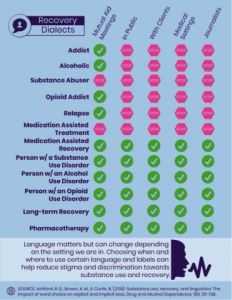
Infographic with comparison of terms and situations in which they should not be used.
Over 21 million Americans have substance use disorder and fewer than 3.8 million individuals receive treatment each year. 28 percent of the individuals who need treatment, but do not receive it, report stigma as a major barrier to accessing care. If we want to destigmatize addiction — a highly stigmatized disorder — then we need a unified language.
The words we use have been shown by researchers to not only negatively influence our attitudes toward people in recovery and people who use substances — to the extent of suggesting that a health condition is a moral, social, or criminal issue — but they also impact access to health care and recovery outcomes.
This article isn’t a mandate for everyone to start policing language, but it was motivated by a genuine desire to look at the evidence: how we speak to someone with substance use disorder matters. In the midst of a public health crisis, we can’t dismiss the use of language as just semantics, trivial, or being overly politically correct. We don’t have that luxury when 64,000 Americans die from drug overdoses each year and over 88,000 die from alcohol-related causes.
Building upon an already existing foundation of work in this field, recovery scientist and researcher Robert Ashford and colleagues conducted a larger study of the general public measuring both implicit and explicit bias elicited by certain common words and phrases, which was published in June. I was fortunate to speak with him about the study, the impact of language, and how we can apply this information to help fight stigma.
The Fix: Let’s say you’re among peers in recovery and you refer to yourself by a term which your study has shown to be a derogatory, like “addict,” “alcoholic,” or “substance abuser.” How does that contribute towards the stigma those in recovery face?
Robert Ashford: This is an interesting question, and one from an evidence perspective, we don’t have exact answers on. Anecdotally, we believe that even though it is probable that this type of language has an impact on things like self-stigma, self-esteem, and a sense of self-worth, it is more important that people have the right to label themselves as they choose, especially as it concerns the recovery community. The fact is that the use of pejorative labels has had a decades-long place in popular mutual-aid programs like AA and trying to tell the mutual aid recovery community what to do isn’t a goal, nor should it be in our minds. At the end of the day though, it is important for people in recovery to understand that the use of such labels may become internalized over time, leading to decreases in self-esteem and such. However, without more evidence, it is merely hypothetical at this point.
In what ways does it impact their lives? For example: their access to, and quality of, healthcare?
Generally, the use of terms such as “substance abuser,” “addict,” and others have been found to be highly associated with negative attitudes (i.e. bias) in the general public, among behavioral health professionals, and in medical professionals. These negative associations ultimately lead to all types of stigma (social and professional) and ultimately to very explicit discrimination. On a personal level, we know that just over 25% of individuals with a severe substance use disorder don’t seek treatment each year due to the belief that they will be stigmatized or discriminated against by their friends, neighbors, or employers. Additionally, this type of bias has also been found to decrease the willingness and efficacy of medical services delivered to patients that have a severe substance use disorder. Access and the quality of treatment in the United States has many barriers and enhancing those barriers through the use of language is an easy fix – just by changing the way we talk!
What would be an alternative, less-stigmatizing term?
Any term that puts the focus on the individual as a human is bound to be less stigmatizing. For example, individuals are not “addicts” or “substance abusers,” but rather, “people with a severe substance use disorder” or a “person who uses substances.” Language changes constantly, but the one commonality in terms of bias and stigma seems to be that when we can restore or focus on the humanity of an individual through our language, we will be speaking from a better place.
How might that term be more empowering to the individual, and in what ways?
As a person in recovery, I can speak personally that when using terms that are rooted in humanity, I get a better sense of myself and the conditions that I have either lived with or am living through. Often times when we are in the midst of a severe substance use disorder, faced with a constant barrage of language that is meant to disempower and dehumanize, we began to internalize those labels. While it is possible in certain settings that these terms are used as a reminder of a previous identity – intending to provide some sense of catharsis in the recovery process, or a mechanism for not returning to a previous state – I think it is equally plausible that we can be reminded and have that benefit by using terms that don’t immediately degrade our very essence as people.
I’m curious how a growth mindset versus a fixed mindset might inform our choices of words? Corollary, how does each mindset inform how we interpret what we hear from others?
This an interesting question, especially in applying the growth and fixed mindset theories from childhood development and education to the field of substance use and recovery. The theory suggests that those who believe they can improve or change (growth mindset) are more likely to engage in activities that allow them to grow, and those that believe they cannot improve or change (fixed mindset) or less likely to do so. In the context of recovery and substance use, this has immense potential to inform how language truly does impact individuals in or initiating recovery. If a person has internalized the negative stereotypes associated with being “an addict,” are they more likely to have a fixed mindset? While there are surely myriad reasons for the challenges faced by people with a severe substance use disorder, mindset may indeed be a big part of it.
You’ve done an incredible amount of work in educating both those in recovery and clinicians about the importance of the language we use. Some of your research features infographics about negative language and presents a positive alternative (below). For those who may need further clarification, what is the difference between pharmacotherapy (or medication to treat substance use disorders) and medication-assisted recovery?
The infographics we made from our results have sure inspired a lot of conversation – which is exactly what we hoped for as scientists! One of the constant topics has been around “medication-assisted treatment,” “pharmacotherapy,” and “medication-assisted recovery.”
Pharmacotherapy is the use of medications to treat a disorder/disease/ailment – specific to our field, this would imply treating a substance use disorder with medications. The term had significantly more positive associations than a similar term, “medication-assisted treatment” from our tests and we wanted to make the suggestion to use it instead.
“Medication-assisted recovery” on the other hand can be considered the use of substance use disorder medications, combined with the use of recovery support services such as MARS recovery meetings, engaging with a peer recovery support specialist, utilizing a recovery community organization, or attending a MAR-friendly 12-step meeting. The biggest difference is that not everyone who uses substance use disorder pharmacotherapy wants, or would consider themselves, in recovery. Keeping the two terms separate gives people an option, and from a research prospective, both terms are associated with the positive and their use isn’t likely to elicit implicit bias among the general public.